
In 2024, competition in the Chinese automotive market has intensified. This year, BYD's economies of scale, AITO's intelligent driving technology, and Xiaomi Auto's late-mover advantage have set benchmarks for many brands, while some others have struggled to keep up.
The transition from oil-powered to electric vehicles is accelerating. The share of new energy vehicles in new car sales rose from 32.8% in January 2024 to 51.1% in July and has stayed above 50% through November. China EV 100 forecasts that total auto sales in China will reach 32 million in 2025, with new energy vehicles still in a crucial phase of scaling up. This indicates that the competition between oil and electric vehicles has entered a stage of balance and mutual restraint. Fuel vehicles will not quickly exit the market, but the competition for market share will intensify.
The changes in the Chinese automotive market are impacting multinational brands' strategies. Some brands plan to reduce their 2025 delivery targets, and Nissan and Honda have officially begun merger negotiations, drawing significant industry attention.
This move represents a strategic attempt by automotive enterprises to collaborate in the face of fierce competition and numerous challenges. This merger will be the largest reorganization in the global automotive industry since the 2021 Fiat Chrysler Automobiles and PSA merger, which created Stellantis valued at 52 billion US dollars.
Hard to make a choice while external and internal
In recent years, the global automotive market has seen significant shifts due to electrification and intelligentization. Companies like Tesla have surged ahead with innovative models and technology, challenging traditional automakers. Stricter environmental regulations and rising consumer demand for new energy vehicles are also pressuring legacy brands to accelerate transformation. Consequently, Japanese giants Honda and Nissan face unprecedented challenges.
At the market level, Honda and Nissan have seen declining performance in major markets like China. In 2023, Honda's global sales reached 3.98 million units, but its Chinese sales fell to 1.23 million units, down 10%. Nissan's Chinese sales dropped by 24%. In the first 11 months of 2024, Honda's Chinese sales were 740,000 units, a 30.7% decrease year-over-year, while Nissan sold 620,000 units, down 10.5%. Both companies have lost market share to local Chinese brands and other competitors.


Nissan achieved past success in the Chinese market with models like Sylphy. However, recent slow product updates and failure to meet growing demands for intelligent and electric vehicles have led to significant sales declines. Honda faces similar challenges.
In product strategy, Nissan has been too conservative in model positioning and failed to meet young consumers' demand for personalization and technology. Meanwhile, Honda has lagged in developing hybrid and electric models, missing early market opportunities.
The financial situation is bleak due to declining sales and increased R&D investment, squeezing profit margins. Facing these internal and external challenges, a merger could be a viable solution for Nissan and Honda to overcome their difficulties.
Hard to merge
The industry is cautious about the potential Nissan and Honda merger. If successful, optimists predict it could create a highly competitive global automotive giant. Resource integration would offer cost advantages, while technological synergy could boost innovation, potentially reshaping Japan's automotive standing and enhancing its competitiveness against European, American, and Chinese automakers.
The cautious observers believe the merger faces significant challenges. Integrating corporate culture and structures may cause short-term chaos, impacting production and sales. Improper handling of product planning and brand positioning conflicts could weaken both parties' original market advantages.

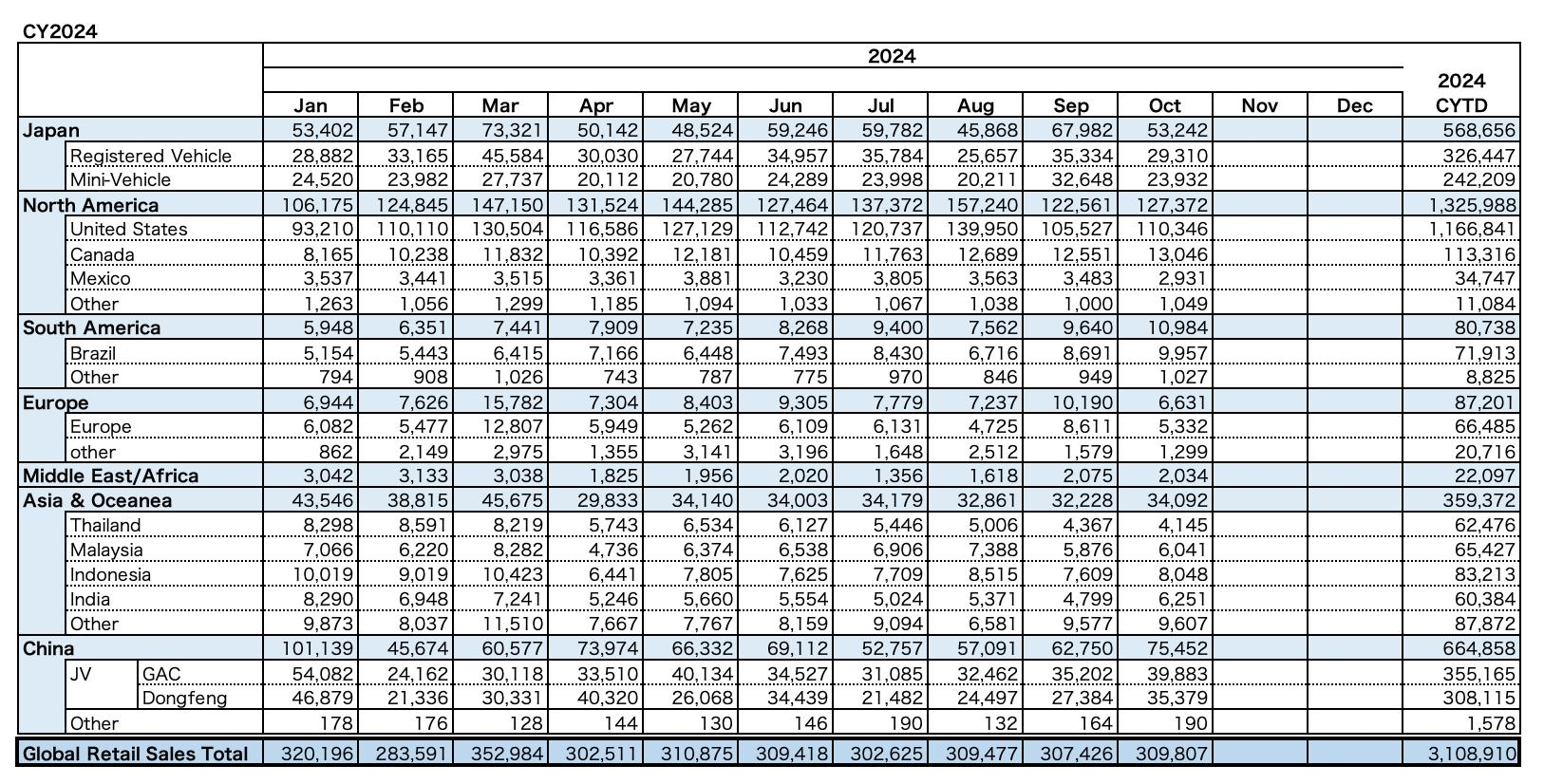 Honda’s Global Retail Sales from January to October, 2024
Honda’s Global Retail Sales from January to October, 2024
Regarding the merger, Carlos Ghosn, former Nissan Motor chairman, expressed doubt about the success of a Honda-Nissan merger in an interview. He is not optimistic about the move. Cui Dongshu, secretary-general of the China Passenger Car Association, also voiced pessimism. Both companies should focus on increasing local R&D investment in China to drive product innovation and leverage the Chinese industrial chain for global growth. They need technological innovation and upgrades rather than just cost reductions through large-scale synergy. Focusing core energy and R&D on the competitive Chinese market will yield better returns.
Some Japanese media believe that the significant differences between the two companies will lead to more problems post-merger. For example, Toyota, a leading Japanese brand, manages its sub-brands as affiliated subsidiaries, creating a structure with one dominant brand and several smaller ones. Based on current market value, in the newly merged company, Honda Motors would hold 77-78%, Nissan Motors 15-16%, and Mitsubishi Motors 6-7%. This suggests Nissan may lose decision-making power and become the subordinate party.
Japanese media noted that Honda is known for its technological innovation, independent decision-making, strong engineering culture, and straightforward management model. In contrast, Nissan, influenced by the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, has a more complex decision-making process with an emphasis on collaboration within the alliance and detailed management, leading to a vertically divided departmental structure. Post-merger, coordination in management structure, decision-making, and communication is essential to avoid slow decision-making and ineffective implementation. These cultural differences may cause conflicts in management philosophy and decision-making approaches, impacting operational efficiency.

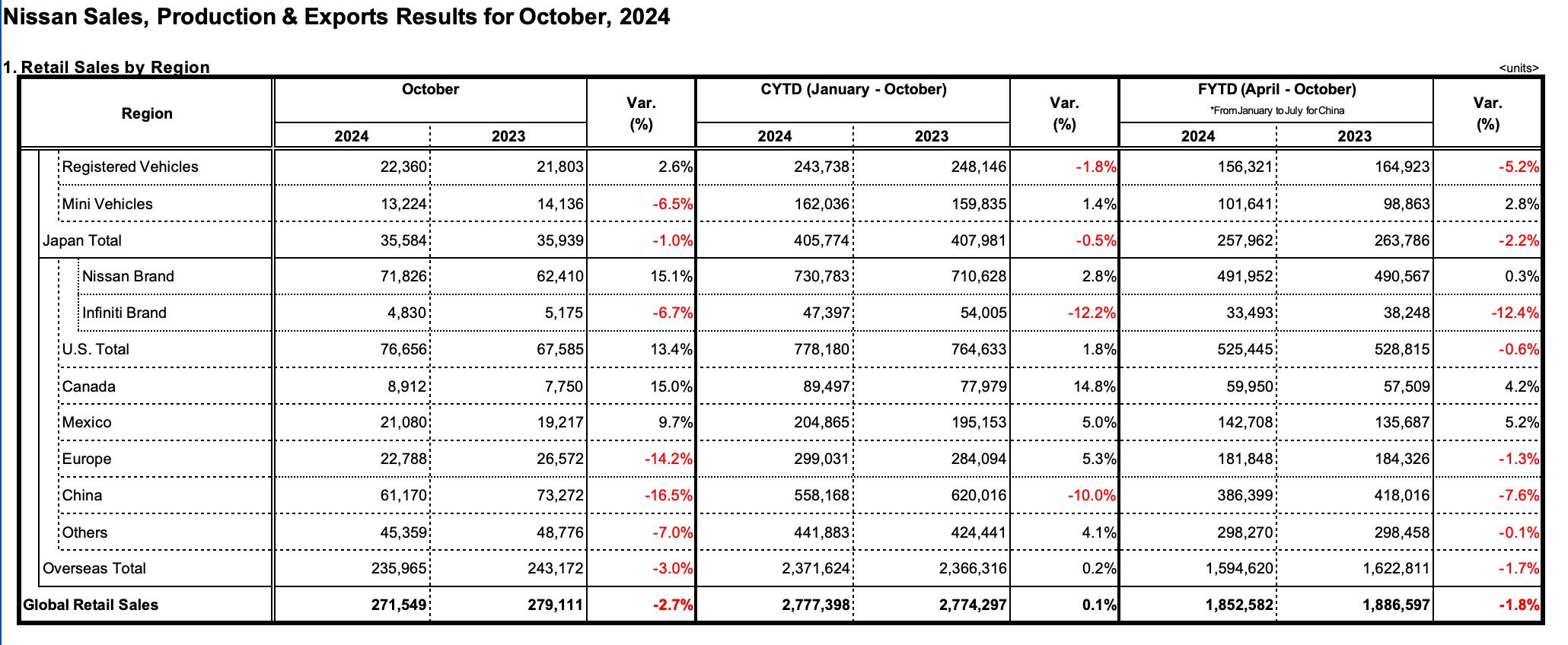 Nissan’s Global Retail Sales from January to October, 2024
Nissan’s Global Retail Sales from January to October, 2024
Honda excels in hybrid technology, particularly with its i-MMD system. Nissan has made significant progress in electrification, notably with the e-POWER range extender. The two technologies differ significantly in approach and application. Integrating and complementing these technologies to create more competitive new energy vehicles is a major challenge. Both companies must also increase investment and R&D in key areas like electrification and intelligentization to stay competitive.
Resources must be reallocated post-merger to optimize R&D resource allocation and prevent duplicate investment and waste. To maintain competitiveness in the new energy market, the focus should be on key technologies like electrification and intelligentization. However, inconsistent R&D directions and resource competition may affect innovation efficiency.


To enhance competitiveness, the merged enterprise must quickly adapt to market changes and allocate resources efficiently to launch products that meet market demands. Japanese media estimates a two-year or longer running-in period due to the large post-merger structure. Maintaining market share and launching competitive products during this time is crucial. Renault, as part of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, will "discuss and consider all options with Nissan" and is open to cooperation between Honda and Nissan, potentially holding a stake in the new company.
In 2025, Chinese auto market players are strengthening their positions and seeking breakthroughs. Changan Automobile's chairman Zhu Huarong noted in a forum that traditional automakers like Honda and Nissan are deepening cooperation due to market competition. This suggests the market is consolidating and challenging many brands, as the industry believes the Chinese market cannot support so many brands.

 Room 1104,Block B,JingBan Building,6 Middle Beisanhuan Road,Xicheng District,Beijing
Room 1104,Block B,JingBan Building,6 Middle Beisanhuan Road,Xicheng District,Beijing
 (8610)62383600
(8610)62383600
 quanqixiang@carresearch.cn
quanqixiang@carresearch.cn
 京公网安备:11010202007638号|京ICP备17032593号-2|Report illegal and bad information:010-65993545-8019 jubao@carresearch.com
京公网安备:11010202007638号|京ICP备17032593号-2|Report illegal and bad information:010-65993545-8019 jubao@carresearch.com
Legal support:Beijing Yingke Law Firm|All rights reserved, DO NOT reproduce without permission